[c++/HTTP] 路由的 前缀树和哈希表 实现
路由
路由指的其实就是 url 和 响应函数 之间的映射关系
在一个服务中,我们可以为多个url以及它的不同的请求方法(如Get、Post等)指定各自的响应函数,当用户向服务器发送某一url的某一请求方法时,执行我们绑定的响应函数。
例如:我的服务有:
Post /user/login -> User.login() 登录接口
Get /user/info -> User.getInfo() 获取用户信息接口
Post /user/info -> User.setInfo() 修改用户信息接口
...
平时使用一些框架时,往往提供了很方便的操作来帮助我们为解决这些映射关系,下面我们就来聊聊如何自己实现一个路由。
基础功能
首先我们先理清楚基本的路由需要实现哪些功能:
根据url和方法,来调用对应绑定的函数。
如果请求的url没有绑定任何函数,则应当返回404,即请求位置不存在
如果请求的url有绑定函数,但该请求的方法却没有绑定函数,则应当返回403,即请求方法不正确。例如:
存在绑定 Post /user/login -> User.login()
收到了一个请求 Get /user/login
/user/login 位置是存在绑定函数的,但应当给Post用的,而请求是Get,请求方法不对应,因此需要返回403错误。
最简单的就只要实现这三种情况就可以了。
思考|数据结构设计
- 实现基础功能的方式很多,但我们肯定会想找最快最好的,下面我们来讨论一下如何设计。
前缀树|字典树
我们常见的url格式经常是这样的:
/user/login/signIn
/user/login/signUp
/user/getInfo
/user/setInfo
/playlist/getInfo
/playlist/setInfo
...
可能你已经发现了一些端倪,一些url总是有相同的前缀,而且我们在给接口取url时也习惯于这样设计。
是的,这非常适合树的结构来存储和查找,因此这里我们来介绍一下如何使用前缀树来设计路由。
我们可以将url按 / 进行分割,然后分割出来的每一个部分作为树的一个节点,如上面的那些url就可以构成如下的树结构:
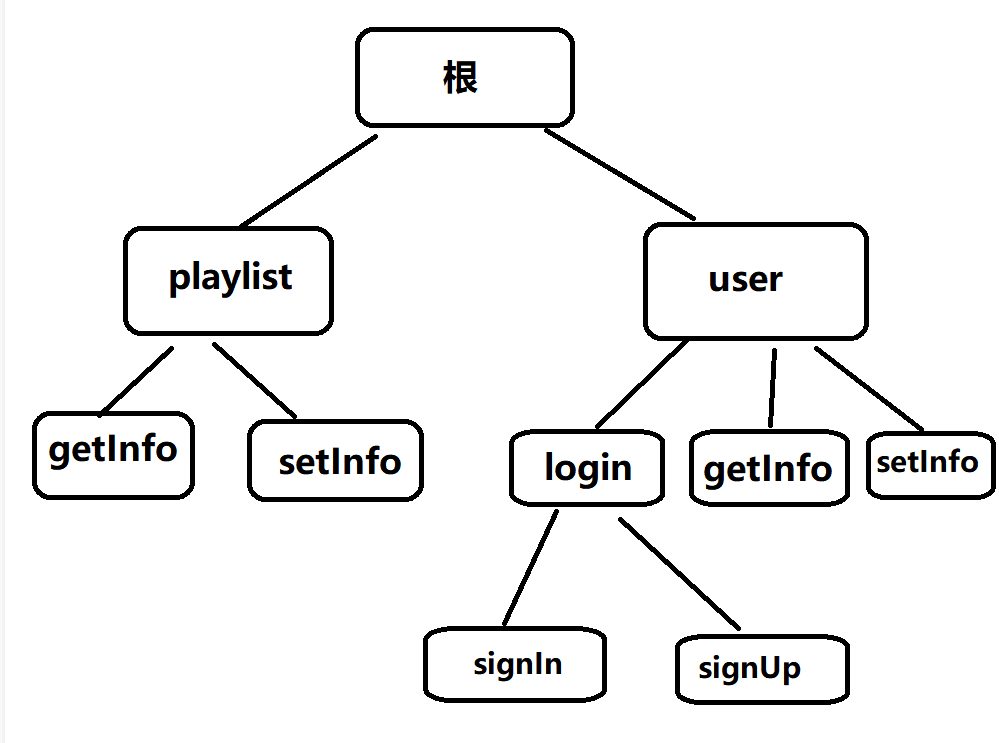
然后每一个节点(包括根节点)都能够绑定自己的请求方法的响应函数。
比如 Post /user/login/signIn就可以对 根->user->login->signIn 节点的Post位置,存放一个响应函数,当服务器收到该url请求时,就可以按路径搜索定位到 signIn 这个节点,并按请求方法来调用该节点保存的响应函数即可。
实际上,我们还可以给每一个节点保留一个 * 的子节点,这样一来,上面这棵树就还能支持这样的路径:/* /user/* /user/login/* ......
这可用于增加一些自定义规则,提高整体的扩展性。这样的设计可以得到很多功能特性支持,本文后面我们会提及一部分。
比如这样设计后,对于 /user/:id 这样的形式就很容易实现。( /user/:id 指的是直接将用户id作为url的path的一部分,而非我们以前的传参的形式 /user?id=123,取而代之的是这样的:/user/123 )
哈希表
HashMap其实应该是第一个想到的解决办法,因为url是字符串,加上快速的需求,脑海里当然会有HashMap浮现。
那么为什么我们没把它作为首选介绍呢,显然它对比前缀树存在一定的问题,下面我们就来聊聊。
在上面的示例中放在哈希表实现也没有问题,在哈希表面前众生平等,而不会像树这样分层,且往往哈希能够一次就找到目标。
这么说的话,好像哈希表才是正路??非也,正因为url在它面前众生平等,它没能将有关联的url联系起来,导致回溯之类的操作比较麻烦。所以当遇到上面提到的 /user/:id 这一类的查找时就犯难了。尤其哈希表对模糊匹配更是无能为力。
结合前缀树和哈希表
前缀树和哈希表各有优劣,那我即想要前缀树的高扩展性,又要哈希表的性能,能否结合起来呢?这里我们就聊聊一种结合的思路。
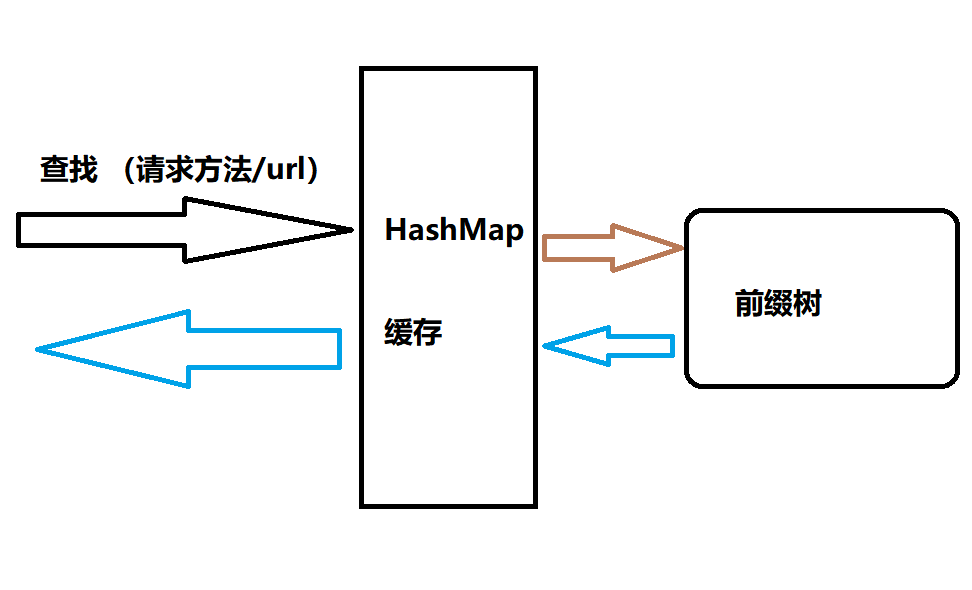
我们可以考虑将前缀树作为路由的实际实现本体,然后用哈希表挡在前面当作缓存:
由于大部分时候,我们项目启动后绝大部分路由位置是不需要改变的,因此这样设计后,第一次请求会需要访问前缀树比较慢,后面的直接可以读到HashMap的缓存记录就快了。
实现思路
首先是前缀树的实现,我们需要它符合最长前缀匹配的规则,比如 请求链接 /user/login/hello 能够匹配这些情况:
/user/*
/user/login/*
/user/login/hello
我们应当匹配得到最后一个,因为它和请求链接最为相似,一般通配符是要比具体字符串低优先级的。
那如果我的请求链接是 /user/login/abc,并且 /user/login/* 并没有绑定响应函数,而是在 /user/* 绑定了响应函数,如何让其匹配得到 /user/* 而非 /user/login/* 然后返回了404呢?
按照生成的前缀树,首先会按这样的路径查找 根->user->login-> [无],来到login节点时,我们发现 没有子节点匹配 abc 这个字符串,则检查 * 节点,但它也没有绑定响应函数;那此时就应当回溯,回退到上一级 user 节点,并检查 user 节点的 * 节点是否有响应函数即可。
是的,相信你已经发现了大概的处理逻辑:首先按着树结构和请求url的/拆分出来的单词进行逐层深入匹配,当来到某一位置,匹配失败时,再回溯检查每一层的 * 节点 的状态。
如果逻辑走完仍然没有找到可用的位置,则应当返回 404(请求位置不存在)
如果找到了目标节点,但该节点对应的请求方法却没有绑定响应函数,则应当返回403(请求方法不正确)
接下来是HashMap如何作为缓存,Map<url, node>,即将url路径作为key,将前缀树查找得到的节点作为value,注意,在这个过程中可以忽略请求方法,只关注请求路径对应的节点是否能查找成功。
大概的思路:首先将url作为key查找HashMap:如果值存在,则直接返回;如果值不存在,则HashMap转给前缀树搜索,前缀树搜索完成后将结果交还,HashMap将其加入缓存记录,然后返回这个节点。对请求方法的检查和匹配,可以放在HashMap返回节点后进行即可。
c++实现
- MyHttpMethod.h,包含Http方法枚举和一些相关操作
#ifndef HTTPMETHOD_H
#define HTTPMETHOD_H
#include <string>
//http请求类型枚举
class MyHttpMethod_e {
public:
static constexpr int
HttpMethod_size = 8, //http请求类型的数量
Get = 1,
Post = 2,
Put = 4,
Delete = 8,
Head = 16,
Options = 32,
Trace = 64,
Connect = 128,
Min = MyHttpMethod_e::Get,
Max = MyHttpMethod_e::Connect;
};
class MyHttpMethodArrItem_s {
public:
int mNum; //在数组中的下标
int mInt; //method的枚举数值
std::string mStr; //类型字符串名称
MyHttpMethodArrItem_s(int in_mNum, int in_mInt, const std::string& in_mStr) {
mNum = in_mNum;
mInt = in_mInt;
mStr = in_mStr;
}
};
//HTTP请求类型数组,便于循环判断
static const MyHttpMethodArrItem_s myHttpMethodArr[MyHttpMethod_e::HttpMethod_size] = {
MyHttpMethodArrItem_s(0, MyHttpMethod_e::Get, "GET"),
MyHttpMethodArrItem_s(1, MyHttpMethod_e::Post, "POST"),
MyHttpMethodArrItem_s(2, MyHttpMethod_e::Put, "PUT"),
MyHttpMethodArrItem_s(3, MyHttpMethod_e::Delete, "DELETE"),
MyHttpMethodArrItem_s(4, MyHttpMethod_e::Head, "HEAD"),
MyHttpMethodArrItem_s(5, MyHttpMethod_e::Options, "OPTIONS"),
MyHttpMethodArrItem_s(6, MyHttpMethod_e::Trace, "TRACE"),
MyHttpMethodArrItem_s(7, MyHttpMethod_e::Connect, "CONNECT")
};
//HTTP请求类型的相关操作方法
class MyHttpMethod_c {
public:
//判断in_m1与in_m2包含的请求类型是否有交集
static bool isAllow(int in_m1, int in_m2);
static bool isAllow(const std::string& in_m1, int in_m2);
static bool isAllow_strOne(const std::string& in_m1, int in_m2);
static bool isAllow(const std::string& in_m1, const std::string& in_m2);
//将包含请求类型的in_str转为int值表示
static int strToInt(const std::string& in_str);
/*将包含请求类型的in_str转为int值表示
* 但要求in_str只包含了一个请求类型
* 否则只返回按HttpMethod_e枚举顺序第一个找到的类型对应的int值
*/
static int strToInt_one(const std::string& in_str);
//将使用int值表示的请求类型转为string表示
static std::string intToStr(int in_int);
/*将使用int值表示的请求类型转为string表示
* 但要求in_int只表示一个请求类型
* 否则只返回按HttpMethod_e枚举顺序第一个找到的类型对应的string
*/
static std::string intToStr_one(int in_int);
static int toIndex_one(int in_method);
static int toIndex_one(const std::string& in_method);
};
#endif- MyRouter.h,路由实现
#ifndef MYROUTER_H
#define MYROUTER_H
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include "MyHttpTask.h"
#include "MyHttpMethod.h"
//路由
class MyRouter_c {
protected:
//路由 树节点
struct RouterTreePort_s {
protected:
public:
/// <summary>
/// 路径
/// </summary>
std::string path;
/// <summary>
/// 对应Http方法的处理函数
/// </summary>
MyHttpProcess_t fun[MyHttpMethod_e::HttpMethod_size];
/// <summary>
/// 子节点
/// </summary>
std::map<std::string, RouterTreePort_s*> child;
RouterTreePort_s(const std::string& in_path = "") noexcept :path(in_path) {
for (int i = MyHttpMethod_e::HttpMethod_size; i-- > 0;)
fun[i] = nullptr;
}
// 返回对应路径节点,不存在则返回nullptr
RouterTreePort_s* get_child(const std::string& in_path, std::string& re_path, bool do_add = false) {
return this->get_child(in_path.c_str(), re_path, do_add);
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取对应路径[in_path]的节点,并返回路由路径到[re_path]
/// </summary>
/// <param name="in_path">待查找路径</param>
/// <param name="re_path">节点真实路由路径;无对应节点时返回空</param>
/// <param name="do_add">当路径对应节点不存在时,是否添加节点</param>
/// <returns>对应路径节点,不存在则返回nullptr</returns>
RouterTreePort_s* get_child(const char* in_path, std::string& re_path, bool do_add = false) {
const char* strptr = in_path, *nextptr = in_path;
for (;;) {
if (*nextptr == '/') {
if (*(nextptr + 1) == '/') {
++nextptr;
}
else
break;
}
else if (*nextptr != '\0') {
++strptr;
++nextptr;
}
else { //strp = '\0',是最后一个子节点
auto it = child.find(in_path);
if (it != child.end()) { //存在子节点
re_path = in_path;
return it->second;
}
else {
if (do_add) {
auto treeptr = new RouterTreePort_s(in_path);
child[in_path] = treeptr;
re_path = in_path;
return treeptr;
}
else {
it = child.find("*");
if (it != child.end()) {
re_path = "*";
return it->second;
}
else {
re_path.clear();
return nullptr;
}
}
}
}
}
// *strp = '/',不是最后一个子节点
std::string str{ in_path, strptr };
++nextptr;
auto it = child.find(str);
if (it != child.end()) { //如果存在子节点
auto re_ptr = it->second->get_child(nextptr, re_path, do_add);
if (re_ptr != nullptr) { //有找到匹配的路径
re_path = str + "/" + re_path;
}
return re_ptr;
}
else {
if (do_add) { //如果需要新建子节点
auto treeptr = new RouterTreePort_s(str);
child[str] = treeptr;
auto re_ptr = treeptr->get_child(nextptr, re_path, do_add);
if (re_ptr != nullptr) {
re_path = str + "/" + re_path;
}
return re_ptr;
}
else { //查找是否有通配符
it = child.find("*");
if (it != child.end()) {
re_path = "*";
return it->second;
}
else { // 无查找结果,清空re_path并返回nullptr
re_path.clear();
return nullptr;
}
}
}
}
/* 使用类型枚举设置处理函数
* 支持同时设置多个类型
*/
bool set_fun_byMethod(const MyHttpProcess_t& in_fun, int in_method) {
size_t donum = 0; //记录设置函数的次数
for (int i = 0; i < MyHttpMethod_e::HttpMethod_size; ++i) {
if (MyHttpMethod_c::isAllow(in_method, myHttpMethodArr[i].mInt)) {
fun[myHttpMethodArr[i].mNum] = in_fun;
++donum;
}
}
if (donum > 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
/* 使用类型下标设置处理函数
* 仅支持一个类型下标
*/
bool set_fun_byIndex(const MyHttpProcess_t& in_fun, int in_index) {
if (in_index >= 0 && in_index < MyHttpMethod_e::HttpMethod_size) {
fun[in_index] = in_fun;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
/* 用数组下标获取函数
* 下表越界时返回nullptr
* 指定下标的函数未定义时返回nullptr
*/
const MyHttpProcess_t& get_fun_byIndex(int in_index) const {
if (in_index >= 0 && in_index < MyHttpMethod_e::HttpMethod_size) {
return fun[in_index];
}
else
return Nullptr_MyHttpProcess;
}
/* 用请求类型获取函数
* 指定请求类型对应的函数未定义时返回nullptr
*/
const MyHttpProcess_t& get_fun_byMethod(int in_method) const {
return this->get_fun_byIndex(MyHttpMethod_c::toIndex_one(in_method));
}
/* 清空子节点
*/
void clear_child() {
for (auto it = child.begin(); it != child.end(); ) {
it->second->clear_child(); //调用子节点的清理
delete (it->second); //释放子节点
child.erase(it);
it = child.begin(); //重置it的指向
}
}
~RouterTreePort_s() {
this->clear_child();
}
};
struct RouterCacheValue_s {
/// <summary>
/// 路由路径
/// </summary>
std::string router_path;
/// <summary>
/// 对应节点
/// </summary>
RouterTreePort_s* treeptr = nullptr;
};
//路由字典树
RouterTreePort_s routerTree;
/* 哈希缓存
* 如果使用缓存接口获取路由位置,获取成功将留下缓存
* 下次使用相同的path获取时直接提取缓存
* 添加或删除路由位置将清空缓存重新生成
*/
std::unordered_map<std::string, RouterCacheValue_s> cacheMap;
/// <summary>
/// 不经过缓存,直接搜索对应路径[in_path]、对应Http方法[in_method]的节点
/// </summary>
/// <param name="in_path">待查找路径</param>
/// <param name="re_path">返回该节点的真实路由路径;节点不存在时返回空</param>
/// <returns>返回查找结果节点</returns>
RouterTreePort_s* get_treep_nocache(const std::string& in_path, std::string& re_path);
public:
MyRouter_c() noexcept :routerTree("/") {}
/* 添加路由
* 允许使用通配符 *
* 允许同时设置多个类型枚举
* 路径中连续的 / 将被视为仅一个 /
* 即 /a//b///c 等同于 /a/b/c
*/
bool add(const std::string& in_path, int in_method, const MyHttpProcess_t& in_fun);
/* 判断是否存在路由位置,使用缓存
* 有,且对应方法有处理函数:返回其处理函数指针,并赋值re_path
* 有,但对应方法没有处理函数:返回nullptr,并赋值re_path
* 没有: 返回nullptr,re_path置空
*/
const MyHttpProcess_t& get(const std::string& in_path, int in_method, std::string& re_path);
/* 判断是否存在路由位置,不使用缓存
* 有,且对应方法有处理函数:返回其处理函数指针,并赋值re_path
* 有,但对应方法没有处理函数:返回nullptr,并赋值re_path
* 没有: 返回nullptr,re_path置空
*/
const MyHttpProcess_t& get_nocache(const std::string& in_path, int in_method, std::string& re_path);
/*移除指定的路由位置,并返回其处理函数
* \param in_method_one 一次调用仅支持移除单一请求类型对应的处理函数
*/
MyHttpProcess_t remove(const std::string& in_path, int in_method_one);
/* 清理缓存
*/
void clear_cache();
//清空路由
void clear();
};
#endif // ! MYROUTER_H- MyRouter.cpp,路由实现
#include "MyRouter.h"
using std::string;
using std::map;
bool MyRouter_c::add(const string& in_path, int in_method, const MyHttpProcess_t& in_fun)
{
string&& method = MyHttpMethod_c::intToStr(in_method);
if (method.empty() == false){ //检查method
this->cacheMap.clear();
const char* strp = in_path.c_str();
while (*strp == '/')
++strp;
string re_path{};
auto treep = this->routerTree.get_child(strp, re_path ,true);
return treep->set_fun_byMethod(in_fun, in_method);
}
else
return false;
}
MyRouter_c::RouterTreePort_s* MyRouter_c::get_treep_nocache(const std::string& in_path, std::string& re_path) {
const char* strp = in_path.c_str();
while (*strp == '/')
++strp;
auto treep = this->routerTree.get_child(strp, re_path);
if (false == re_path.empty()) {
re_path = "/" + re_path;
}
return treep;
}
const MyHttpProcess_t& MyRouter_c::get_nocache(const std::string& in_path, int in_method, std::string& re_path) {
auto treep = this->get_treep_nocache(in_path, re_path);
if (treep != nullptr) { //判断是否存在路由位置
const auto& fun = treep->get_fun_byMethod(in_method);
return fun;
}
return Nullptr_MyHttpProcess;
}
const MyHttpProcess_t& MyRouter_c::get(const std::string& in_path, int in_method, string& re_path)
{
auto refind = this->cacheMap.find(in_path);
MyRouter_c::RouterTreePort_s* treeptr = nullptr;
if (refind != this->cacheMap.end()) {
treeptr = refind->second.treeptr;
re_path = refind->second.router_path;
}
else
treeptr = this->get_treep_nocache(in_path, re_path);
if (treeptr != nullptr) { //判断是否存在路由位置
const auto& fun = treeptr->get_fun_byMethod(in_method);
if (fun) {
this->cacheMap.insert(
{
in_path,
{
re_path,
treeptr
}
});
}
return fun;
}
return Nullptr_MyHttpProcess;
}
MyHttpProcess_t MyRouter_c::remove(const std::string& in_path, int in_method) {
string&& method = MyHttpMethod_c::intToStr(in_method);
if (method.empty() == false) { //检查method
const char* strp = in_path.c_str();
while (*strp == '/')
++strp;
string re_path{};
auto treep = this->routerTree.get_child(strp, re_path, false);
if (treep) {
this->cacheMap.clear();
int index = MyHttpMethod_c::toIndex_one(in_method);
const auto& fun = treep->get_fun_byIndex(index);
treep->set_fun_byIndex(nullptr, index);
return fun;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
void MyRouter_c::clear_cache() {
this->cacheMap.clear();
}
void MyRouter_c::clear()
{
this->routerTree.clear_child();
}